
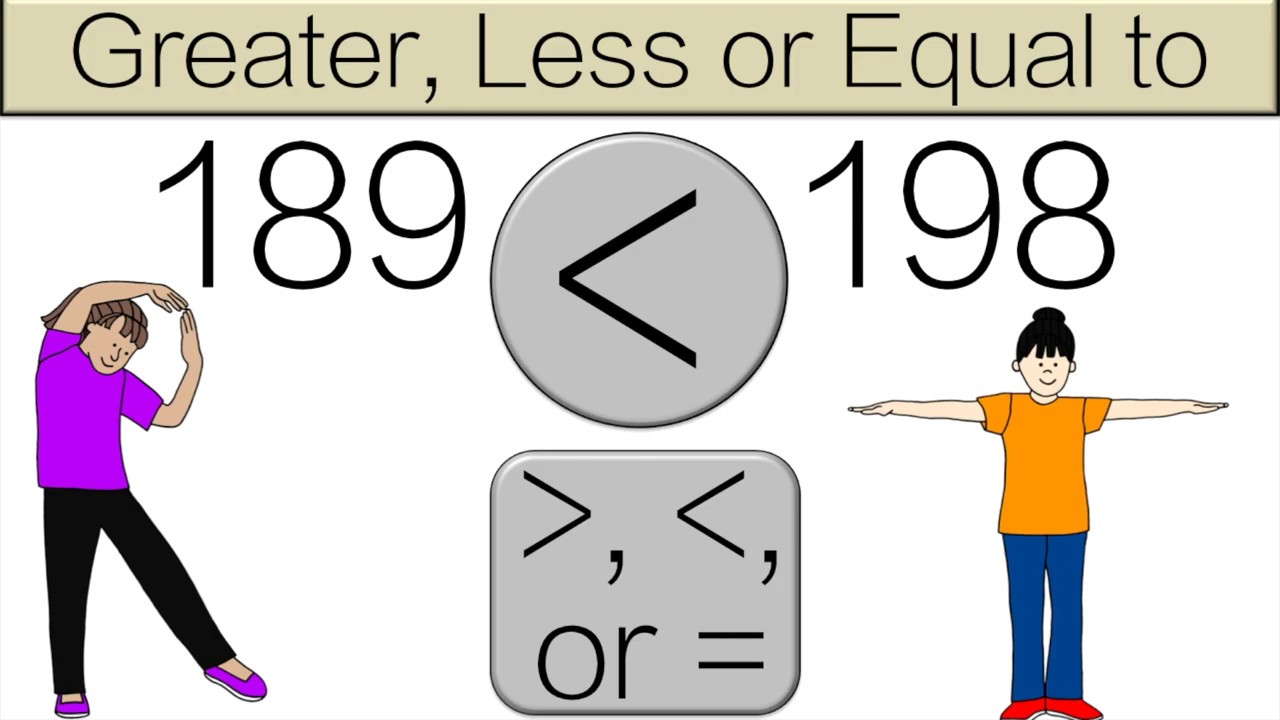
- #Greater than or equal to how to#
- #Greater than or equal to code#
The above quick guide provides some useful shortcuts and alt codes on how to type the Greater than or equal to sign on both Windows and Mac. These keystrokes work in MS Word, Excel and PowerPoint, on both Windows and Mac.īelow table contains all the shortcuts you need to type the Greater than or equal to Symbol on keyboard. Greater than or equal to alt codes) using the numeric keypad, then let go of the Alt key. For Windows users, simply press down the Alt key and type 242 (i.e. To type the Greater than or equal to symbol on Mac, press Option + shortcut on your keyboard. Greater than or equal to Symbol Quick Help Using insert Symbol dialog box (Word, Excel, PowerPoint).
 Copy and Paste Greater than or equal to sign.
Copy and Paste Greater than or equal to sign.  Using the Greater than or equal to symbol Shortcut (Mac and Windows).
Using the Greater than or equal to symbol Shortcut (Mac and Windows). #Greater than or equal to code#
Using the Greater than or equal to symbol Alt Code (Windows Only). Type Greater than or equal to symbol in Word/Excel. Greater than or equal to Symbol Quick Help. If one of the inputs is a multidimensional raster and the other input is a constant, the operator will perform the operation for all slices for all variables against the constant value, and the output will be a multidimensional raster. If both inputs have one variable but different names, set the matchMultidimensionalVariable geoprocessing environment to False to perform the operation. The variables in the inputs must have same dimensions or common dimension but no uncommon dimensions. If both inputs are multidimensional rasters with same number of variables, the operator will perform the operation for all slices with same dimension value, and the output will be a multidimensional raster. If one of the inputs is a multiband raster and the other input is a constant, the operator will perform the operation against the constant value for each band in the multiband input, and the output will be a multiband raster. The number of bands in each multiband input must be the same. If both inputs are multiband rasters, the operator will perform the operation on each band from one input, and the output will be a multiband raster. If both inputs are single-band rasters, or one of the inputs is a constant, the output will be a single-band raster. The order of the input is relevant for this operator. Two inputs are necessary for the evaluation to take place. For more information, see complex statement rules section of Building complex statements. To avoid this potential problem, use appropriate parentheses in the expression so that the execution order of the operators is explicitly defined. When multiple Relational and/or Boolean operators are used consecutively in a single expression, in some cases, it may fail to execute. To change the order of execution, use parentheses. Therefore, when Boolean operators are used in the same expression as Relational operators, the Boolean operators will be executed first. In the relational evaluation, if the condition is true (the first input value is greater than or equal to the second input value), the output is 1 if it is false, the output is 0. The relational greater-than-or-equal-to operation evaluates the first input value in relation to the second input value on a cell-by-cell basis within the Analysis window.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
